Nervous System
Breadcrumb
Discover the Nervous System
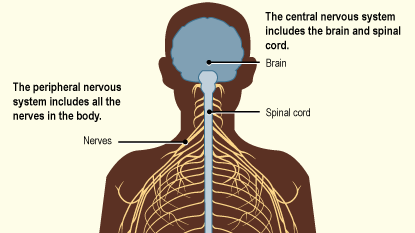 The nervous system plays a role in nearly every aspect of our lives. It guides everyday activities such as waking; automatic activities such as breathing; and complex processes such as thinking and reading. Studying and understanding the nervous system is important because it affects so many areas of human health and well-being.
The nervous system plays a role in nearly every aspect of our lives. It guides everyday activities such as waking; automatic activities such as breathing; and complex processes such as thinking and reading. Studying and understanding the nervous system is important because it affects so many areas of human health and well-being.
The NNLM Reading Club selection of books looks at neuroscience through the lens of people living with a neurological disorder. The authors share how they discovered their neurological condition and how they manage their health.
Help raise awareness in this field of science by reading and discussing one of the memoirs. Then learn more using information from the National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, and other trustworthy resources.
 Discover MedlinePlus
Discover MedlinePlus
MedlinePlus is a service of the National Library of Medicine, the largest biomedical library in the world. Use Medlineplus.gov anywhere, anytime, on any device - for free - to discover high-quality health and wellness information that is reliable, easy to understand, and free of advertising, in both English and Spanish.
Discover information on:
Discover NIH
 The National Institutes of Health (NIH), a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is the nation’s medical research agency — making important discoveries that improve health and save lives. NIH is made up of 27 Institutes and Centers, each with a specific research agenda, often focusing on particular diseases or body systems.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH), a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is the nation’s medical research agency — making important discoveries that improve health and save lives. NIH is made up of 27 Institutes and Centers, each with a specific research agenda, often focusing on particular diseases or body systems.
The primary NIH organization for research on Degenerative Nerve Diseases is the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Its mission is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use the knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS supports research on more than 600 neurological diseases. Use the Health Information Search for a Disorder feature to learn about signs and symptoms and the latest scientific research on more than 250 disorders such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Cerebral Palsy, Multiple Sclerosis, or Parkinson's Disease.
What does the nervous system do? | NIH Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
Research and Therapy
In this NIH audio recording, a woman shares her experience living with MS and participating in a research study.
- Clinical trials and observational studies are the two main types of clinical research. Clinical trials, also called interventional trials, usually focus on evaluating new treatments, while observational studies generally give researchers a better understanding of how a disease progresses with current treatment options. To learn more, use the NIH Clinical Trials and You website. Then use NIH ClinicalTrials.gov to find a clinical research study and information about their results.
- New NIH study may help predict those at risk for severe MS | NIH MedlinePlus Magazine | January 8, 2020
- Cerebral palsy can't be cured, but treatment often improve a person's capabilities. Read about common treatments in What are common treatments for cerebral palsy? Find a PM&R Physician
Discover More
Conversations are a meaningful way to build connection, support, and understanding among community and family. All Our Voices is a toolkit aimed to inspire people to share and preserve their health and wellness stories. The project is made possible with funding from the National Library of Medicine and a partnership between the NNLM All of Us Program Center (NAPC) and StoryCorps. Browse the Toolkit
In this StoryCorp audio recording, a woman and her two daughters discuss her experience living with ALS. StoryCorps, NPR’s Morning Edition, May 6, 2016

BrainFacts.org is an educational website from the Society for Neuroscience. Discover puzzles and games and interact with a 3D image of the brain.
Featured Books



Terms of use: Network of the National Library of Medicine (NNLM) staff offer these health discussion resources for educational use. The materials included do not necessarily reflect the views or opinions of the author, publisher, or the sponsoring agencies of the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
